Treatment Of Pathological Gambling A Critical Review Of The Literature
- Treatment Of Pathological Gambling A Critical Review Of The Literature Answer
- Treatment Of Pathological Gambling A Critical Review Of The Literature Pdf
Treatment Of Pathological Gambling A Critical Review Of The Literature Answer
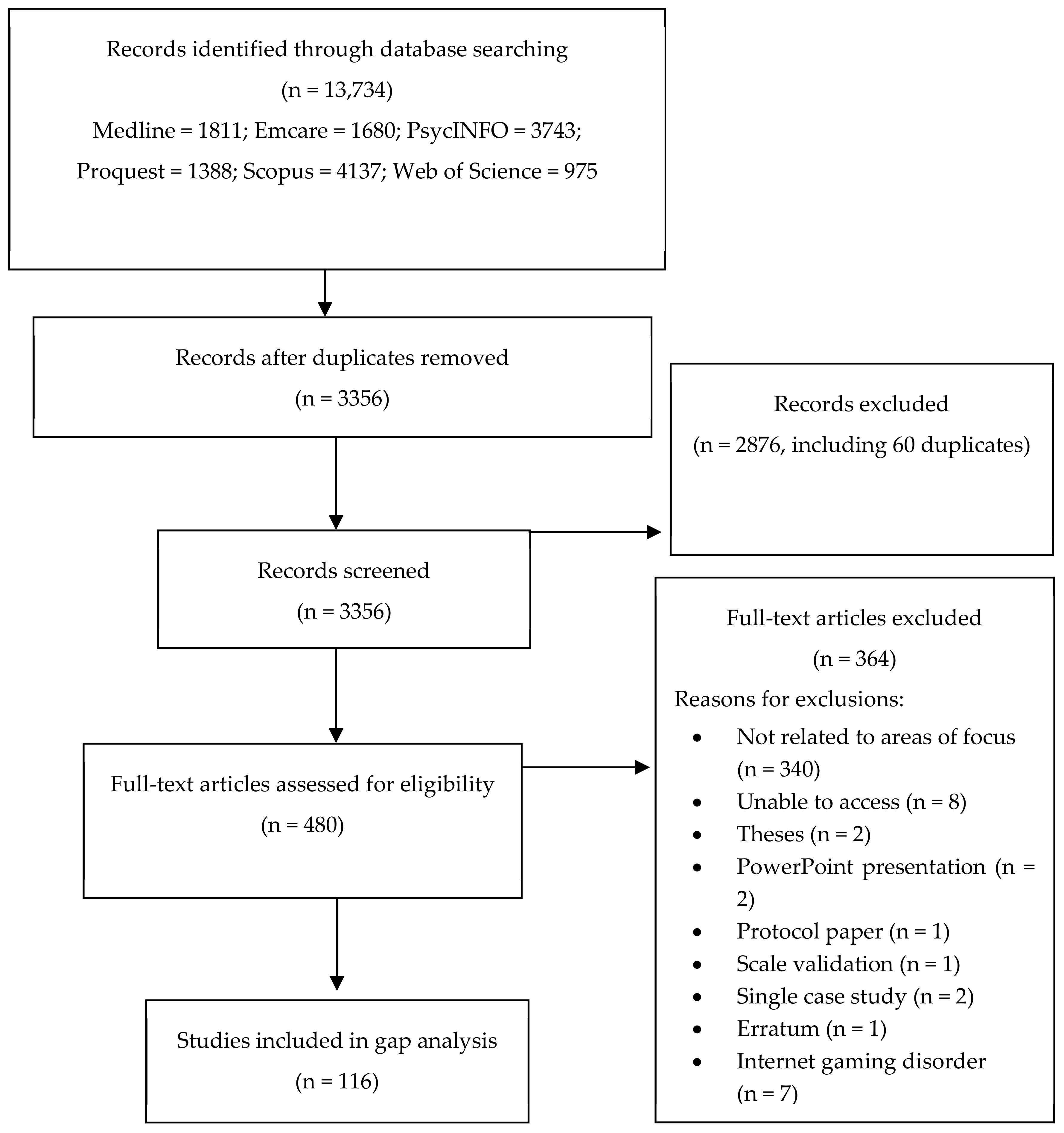
Aims To investigate the short‐ and long‐term effect of psychological treatments of pathological gambling and factors relating to treatment outcome. Design and setting This study provides a quantitative meta‐analytical review of psychotherapeutic treatments of pathological gambling. Studies were identified by computer search in the. With such high prevalence estimates of pathological gambling (see Shaffer et al., 1997 for a comprehensive critical review of the North American gambling prevalence literature), there is an urgent need for effective treatments for this increasingly common psychiatric disorder.
Pathological Gambling explores America's experience of gambling, examining: The diverse and frequently controversial issues surrounding the definition of pathological gambling. Its co-occurrence with disorders such as alcoholism, drug abuse, and depression. Its social characteristics and economic consequences, both good and bad, for communities. Undertake a review of the literature on mood disorders and problem gambling. Intended Audience This review has been undertaken to provide mood disorders researchers and clinicians with an orientation to the current research linking problem gambling and mood disorders. Objective By undertaking a critical review of the literature, we also hope to.
| Title | |
| Authors | |
| Published in | Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2011, vol. 17, no. 14, p. 1389-95 |
| Abstract | Given the rates of pathological gambling and its impact on affected individuals and their relatives, effective treatments are needed. There are, however, no approved pharmacological treatments for pathological gambling. This paper describes the development of pharmacological treatments for pathological gambling and is based on a review of the literature published in the past 10 years. Important studies were carried-out on antidepressants, mood stabilizers, and antipsychotic agents. In the absence of comorbid psychiatric disorder, these studies did not conclude to the efficacy of these psychotropic drugs. A possible efficacy of opiate antagonist treatment for pathological gambling has been replicated in a number of placebo-controlled studies. Preliminary results on N-acetyl cysteine, Memantine and Topiramate produced significant improvement for pathological gamblers and may open new avenues for treatment. |
| Keywords | Animals — Antidepressive Agents/therapeutic use — Antimanic Agents/therapeutic use — Antipsychotic Agents/therapeutic use — Drug Design — Gambling/drug therapy/psychology — Humans — Psychotropic Drugs/therapeutic use |
| Identifiers | |
| Full text | This document has no fulltext available yet, but you can contact its author by using the form below. |
| Structures | Faculté de médecine / Section de médecine clinique / Département de psychiatrie |
| Research group | Abus de substances (834) |
| Citation (ISO format) | ACHAB, Sophia, KHAZAAL, Yasser. Psychopharmacological treatment in pathological gambling: a critical review. In: Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2011, vol. 17, n° 14, p. 1389-95. https://archive-ouverte.unige.ch/unige:92561 |
Deposited on : 2017-03-14
| Format | : |
| Citation style | : |
Treatment Of Pathological Gambling A Critical Review Of The Literature Pdf
Abstract
The legalization and availability of new forms of gambling are increasing in most Western countries. This trend has contributed to the fact that more individuals are developing gambling problems. As a result, there is a need for effective treatments. Although gambling treatment dates several decades, few empirically supported treatments for pathological gambling have been developed. This critical review includes only controlled treatment studies. The primary inclusion criterion was randomization of participants to an experimental group and to at least 1 control group. Eleven studies were identified and evaluated. Key findings showed that cognitive–behavioral studies received the best empirical support. Recommendations to improve gambling treatment research include better validated psychometric mea-sures, inclusion of process measures, better definition of outcomes, and more precise definition of treatments. The legalization of new types of gambling, which can be defined as an attempt to win money by staking money on an uncertain event, is increasing in most Western countries. With prevalence rates hovering between 1 % and 2%, the increased availability of gambling is expected to lead to greater numbers of people devel-oping gambling problems. Pathological gambling was officially recognized in 1980 with the publication of the third edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM–III; American Psychiatric Association, 1980); it was classified as an impulse control disorder. Pathological gambling is characterized by a loss of control over gambling, deception about the extent of one’s involvement with gambling, family and job disruption, theft, and chasing losses, or the effort to win back money lost while gambling (American Psychiatric Association, 1994). It is now acknowledged that the prevalence of pathological gambling is related to the availability of gambling opportunities, legal or illegal